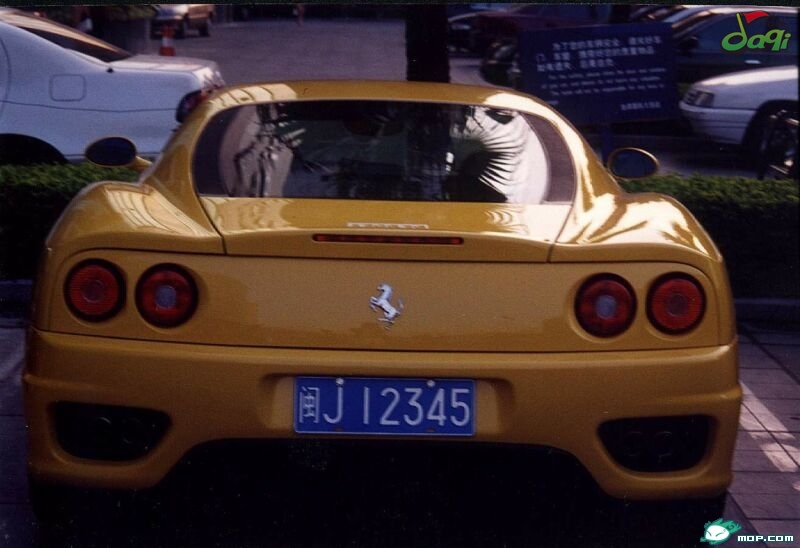
为了做车牌识别训练,先单独研究下怎么从照片里扣出车牌区域。
大概思路:转化成灰度图、使用高斯平滑、中值滤波、Sobel边缘化检测、膨胀轮廓、腐蚀细节、轮廓筛选、保存轮廓区域原图。
代码如下:
vim cut_platenumber.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
# 从下载的图片里扣出车牌区域
# sh clear.sh && python cut_platenumber.py >log/cut_platenumber.log
import uuid
import os
import copy
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
class CutPlateNumber:
"""从下载的图片里扣出车牌区域"""
def preprocess(self, gray, name=''):
"""形态学变换的预处理"""
print '__preprocess__'
# 高斯平滑
gaussian = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (3, 3), 0, 0, cv2.BORDER_DEFAULT)
self.write_image(gaussian, name, 'gaussion')
# 中值滤波
median = cv2.medianBlur(gaussian, 5)
self.write_image(median, name, 'median')
# Sobel算子,X方向求梯度,对图像进行边缘检测
#sobel = cv2.Sobel(median, cv2.CV_8U, 1, 0, ksize=3)
sobel = cv2.Sobel(median, cv2.CV_16S, 1, 0, ksize=3)
sobel = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobel)
# 二值化
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(sobel, 170, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
self.write_image(binary, name, 'threshold')
# 膨胀和腐蚀操作的核函数
element1 = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9, 1))
element2 = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9, 7))
# 膨胀一次,让轮廓突出
dilation = cv2.dilate(binary, element2, iterations=1)
self.write_image(dilation, name, 'dilation')
# 腐蚀一次,去掉细节
erosion = cv2.erode(dilation, element1, iterations=1)
self.write_image(erosion, name, 'erosion')
# 再次膨胀,让轮廓明显一些
dilation2 = cv2.dilate(erosion, element2, iterations=2) #iterations设置太大但车牌区域很小时非车牌区域容易边缘连片过度,设置太小但车牌占比过大时容易省简称和后边连不上
self.write_image(dilation2, name, 'dilation2')
return dilation2
def find_region(self, img, imagePath='', name=''):
"""查找车牌所在区域"""
print '__find_region__'
# 查找轮廓
binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 轮廓筛选
region = {}
standard_w_h_retio = 45/15 #标准车牌宽45cm/高15cm=3
standard_full_retio = 0.2 #常见车牌占图片大小
min_ratio_diff = 99 #与标准车牌长宽比差异最小的值*在图像中的占比大小
img_regins = cv2.imread(imagePath) #所有轮廓叠加对象
for i in range(len(contours)):
cnt = contours[i]
# 计算该轮廓的面积
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
# 面积小的都筛选掉
if (area < 2000):
continue
# 找到最小的矩形,该矩形可能有方向
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
# box是四个点的坐标
box = cv2.cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
#print box
# 不规则形状转矩形(取左上角最小和右下角最大坐标)
xs = [box[0, 0], box[1, 0], box[2, 0], box[3, 0]]
ys = [box[0, 1], box[1, 1], box[2, 1], box[3, 1]]
xs_sorted_index = np.argsort(xs)
ys_sorted_index = np.argsort(ys)
#print xs,xs_sorted_index
#print ys,ys_sorted_index
x1 = box[xs_sorted_index[0], 0] - 20 #左侧省简称部分边缘检测效果不太好,轮廓往左多取一点
y1 = box[ys_sorted_index[0], 1]
x2 = box[xs_sorted_index[3], 0]
y2 = box[ys_sorted_index[3], 1]
if x1 < 1: x1 = 1
if y1 < 1: y1 = 1
# 计算矩形宽高比
width = abs(x2 - x1)
height = abs(y2 - y1)
wh_ratio = float(width) / float(height)
#计算矩形在大图中的像素占比
full_ratio = float(width*height) / float(img.shape[0] * img.shape[1])
#计算矩形在图像中的上下位置与图片大小的匹配合理性(值越小表示越合理)
postion_right_ratio_y = abs(0.5 - float(y2-height/2)/img.shape[1]) * abs(full_ratio - standard_full_retio) #上下位置与图片大小合理性
postion_right_ratio_x = abs(0.5 - float(x2-height/2)/img.shape[0]) * abs(full_ratio - standard_full_retio) #左右位置与图片大小合理性
#postion_right_ratio = (postion_right_ratio_y**2*600 + postion_right_ratio_x**2*400)/2 #放大合理性的差值,上下权重高些
postion_right_ratio = (postion_right_ratio_y*0.6 + postion_right_ratio_x*0.4)/2 #放大合理性的差值,上下权重高些
#复合权重比(高宽比与标准的差值、图像位置与图像大小的合理性)
ratio = abs(wh_ratio - standard_w_h_retio)*0.03 + postion_right_ratio * 0.97
print abs(wh_ratio - standard_w_h_retio),postion_right_ratio
#宽高比及拍照框占比过滤
print i,area,'['+str(x1)+','+str(y1)+' '+str(x2)+','+str(y2)+']',round(wh_ratio,2),round(full_ratio,3),round(postion_right_ratio_x,2),round(postion_right_ratio_y,2),round(postion_right_ratio,2),round(ratio,4)
if (wh_ratio < standard_w_h_retio - 1.2 or wh_ratio > standard_w_h_retio + 2) or (full_ratio < 0.015 or full_ratio > 0.5): #高宽比>2.3 && <5; 拍照框在整图中的占比应>5% && <50%
continue
# 矩形轮廓标记图
img_regin = cv2.imread(imagePath)
cv2.rectangle(img_regin, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2) #单轮廓
cv2.rectangle(img_regins, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2) #轮廓叠加
cv2.putText(img_regins, str(i)+' '+str(round(ratio,4)), (x1+3, y1+15), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 255), 1) #轮廓叠加图上标记轮廓序号
self.write_image(img_regin, name, 'regin'+str(i))
if ratio < min_ratio_diff: #保存复合权重最合理的那个轮廓
min_ratio_diff = ratio
region = {'x1':x1,'x2':x2,'y1':y1,'y2':y2}
self.write_image(img_regins, name, 'regin') #轮廓叠加图像保存
return region
def write_image(self, img, name, step='', path='tmp'):
"""保存图片并打印"""
if False:
return
if step != '':
img_file = './data/'+path+'/'+name.split('.')[0]+'.'+step+'.'+name.split('.')[1]
else:
img_file = './data/'+path+'/'+name
cv2.imwrite(img_file, img)
print img_file
def start(self, imagePath, name):
"""开始裁剪"""
print "START\t" + imagePath
# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread(imagePath)
# 转化成灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
self.write_image(gray, name, 'gray')
# 形态学变换的预处理
dilation = self.preprocess(gray, name)
# 查找车牌区域
region = self.find_region(dilation, imagePath, name)
print region
if len(region) > 0: #车牌轮廓查找成功
# 从灰度图中扣取轮廓矩形并缩放
img_plate = cv2.resize(gray[region['y1']:region['y2'], region['x1']:region['x2']] ,(180, 60))
# 保存车牌区域抠图结果
save_path = 'images_train'
if random.random() < 0.1: #10%放到测试集
save_path = 'images_test'
self.write_image(img_plate, name, path=save_path)
print "FOUND PLATE NUMBER!\t" + name
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = './data/download_rename/'
cutPlateNumber = CutPlateNumber()
# 获取原图列表
imgs = os.listdir(img_path)
for img in imgs:
#img = '辽B48599.jpg'
cutPlateNumber.start(img_path + img, img)
#break单测结果:
各步骤效果图:
原图:
灰度图:
高斯平滑:
中值滤波:
sobel边缘检测+二值化:
轮廓膨胀一次:
腐蚀细节:
再次轮廓膨胀:
轮廓转换矩形后,筛选出的高宽比最接近车牌的区域:
序号 面积 [x1,y1 x2,y2] 宽高比 面积占比 上下位置与图片大小合理性 左右位置与图片大小合理性 平均合理性 复合权重比
3 8226.5 [291,366 483,437] 2.7 0.031 0.05363 0.00042 0.011 0.0194
从灰度图对应位置中扣取轮廓矩形并缩放:
这个方法的关键点在边缘检测后的膨胀腐蚀和轮廓的筛选,可以通过调节preprocess和筛选参数来优化扣图效果。
yan 18.12.4 23:45
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/sunny2038/article/details/9170013